A Center of Asia, Seoul Metropolitan
The history of the city of Seoul dates back approximately 2,000 years, to when Wiryeseong, the capital of Baekje, was located on the banks of the Hangang River in the southeastern part of what is now Seoul. Development of the city began in earnest once it was appointed the capital of the Joseon Dynasty (1392 - 1910) in 1394.
The framework for modern-day Seoul began to emerge as the construction of electrical facilities, railroads, streetcar tracks, parks, waterworks systems, schools, and hospitals commenced at the end of the 19th century with the opening of the port. However, Seoul soon came under the influence of Japanese colonialism (1910 - 1945). This was followed by gradual industrialization, which in turn led to the formation of illegal settlement areas around the city. With these peripheral regions quickly being considered as within the scope of the city, Seoul began to transform into a new residential zone. After Korea achieved independence in 1945, the city was officially renamed Seoul Metropolitan City. However, as the Korean War broke out, the city fell into ruin.
In the 1950s, Seoul rapidly grew out of the ashes of the war and, supported by rapid economic growth, it advanced to become a global megalopolis in just half a century. While it took a century for many European countries to industrialize, Korea accomplished the same in less than 30 years. In only 50 years, Seoul overcame various urban problems to grow and advance into a smart city where 10 million people live comfortably.
Seoul’s contemporary development can be divided largely into three phases. From the 1960s - 1970s, Seoul experienced serious urban issues, such as traffic congestion, environmental pollution, formation of illegal settlement areas, and housing shortages, as a result of the extensive population inflow and lack of social infrastructure. To resolve these issues, the Seoul Metropolitan Government focused on establishing a basic infrastructure by expanding roads, building apartment complexes in illegal settlement areas, and constructing the Cheonggye Overpass and Yeouido Island.
During the 1980s - 1990s, the Seoul Metropolitan Government embarked on a series of active urban improvement and city beautification policies in line with Korea hosting the Asian Games in 1986 and the Olympic Games in 1988. On the one hand, a general development plan for the Hangang River was drawn up and the Gangbyeonbuk-ro and Olympic-daero roads were built running along the river. At the same time, the Seoul Metropolitan Government opened subway lines 2 - 8 and established large-scale apartment complexes in Gangnam, Mok-dong, Godeok-dong, Gaepo-dong, and Sanggye-dong in order to respond to the explosive increase in housing demand among the middle class. As a result of this extensive infrastructure development project, Seoul was able to secure a considerable, high-standard urban infrastructure network consisting of public transportation, roads, waterworks, and sewage systems. However, the relentless development also produced some serious side effects, such as destruction of the natural environment, damage to historical resources, and the breakdown of communities.
In the 2000s, with the development of Informational Technology and an increase in citizens’ demand for improved quality of life, Seoul’s urban management policy took a shift towards creating a sustainable city with advanced IT. In tandem with several park development projects, such as the Cheonggyecheon Stream restoration and Seoul Forest development project, the Seoul Metropolitan Government’s administration became digitized. Recently, as economic growth has slowed down and the social environment has changed due to aging of the population along with other factors, Seoul underwent a paradigm shift in its policies towards urban regeneration. This led to the promotion of the Seoullo 7017 and Sewoon Shopping Center regeneration projects.
Seoul's a historic graph on growth development stages
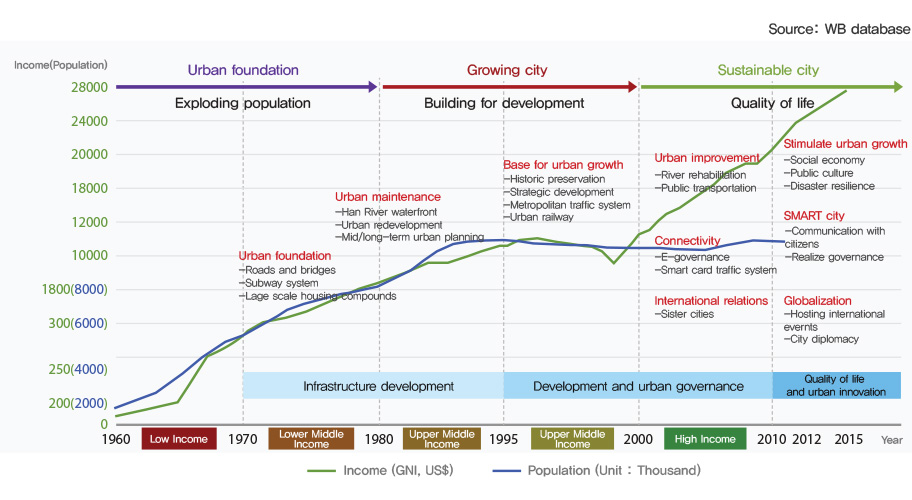
Urban foundation (1960 ~ 1980)
Seoul Built urban infrastructure according to population increase.
Seoul focused financial plan, water management, and stream and river reformation
- Main Urban Development Plans : Gangnam development plan(1970), Yeouido development plan (1971)
- Main projects : Cheonggyecheon covering(1966), Cheonggye Expressway construction(1967),
Han River Bridges (Yanghwa: 1966, Hannam: 1969), West disposal plant(1972), Subway line 1(1974)
Growing City (1980~2000)
Seoul prepared infrastructure for expected population and improved downtown environment on the foundation.
- Main Urban Development Plans : Han river comprehensive development projects(1982), Development of Apartment complexes, Han river sewage management(1987), 180 thousands residence construction(1989)
- Main projects : Subway line 2, 3, 4 (1984 ~ 1985), separate garbage collection(1992), Bus card (1996)
Smart & Sustainable City (2000 ~ present)
Transfer to software-centered policy from hardware-centered policy.
- Main Urban Development Plans : Seoul’s e-Government(2000~ Continue), Seoul e-Government toward Smart City, Big Data-based Administration, 2030 Seoul Plan, Historical Heritage Conservation Projects
- Main projects : Online civil service offer (2000), Cheonggyecheon Restoration(2004), Public transportation system reformation(2004), Waste management system of Seoul(2005), Subway screen door(2006 ~ present), Eco-Mileage System(2008), the 120 Dasan Call Center(2012), Car Sharing in Seoul (Nanum-Car)(2013), Owl Bus Based on Big Data(2013), Safer City for Women Project(2013)
Go To SEOUL METROPOLITAN GOVERNMENT Official Homepage