Seoul e-Government toward a Smart City
ISSUES
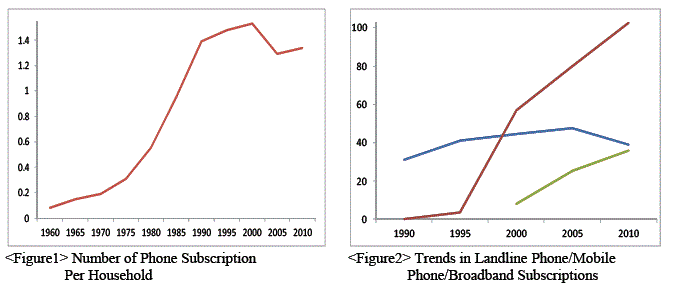
The computer ownership rate has increased 17.6 times from 5% in 1985 to 86% in 2009. Until the mid-1960s one in every ten households had a phone, but this had increased to 0.54 phones per household in 1997, then to 1.56 in 2000, and by 2007, there were 1.34 phones per household. Much of this growth can be attributed to the proliferation of mobile phones since the 1990s, when 0.2 persons of every 100 had one in 1990, and 105.5 of every 100 by 2011. In 2000, 8.2 of every 100 people had a broadband internet connection, but this had dramatically increased to 35.9 of every 100 by 2011, or by a multiple of 4.4.
As a means to achieve governmental efficiency and innovation, transparency and accountability, accessibility to government and civic participation, Seoul's e-government policy seeks to encourage the active engagement of citizens in ICT, while building a cooperative relationship between the Seoul Metropolitan Government (SMG) and city residents.
SOLUTIONS
Solution 1: Government-driven promotion and Seoul’s compliance
Solution 2: Coordination and Direction via the SMG Information System Planning Bureau
Solution 3: Enhanced Paradigm: From efficiency to transparency and citizen participation
ACHIEVEMENTS
Ranked No. 1 in Global E-Governance Survey for five consecutive years
A research study conducted by Rutgers University has identified Seoul as the top city in the field of e-government, where it ranked number 1 in terms of usability, service, and citizen participation - the best among cities in OECD countries.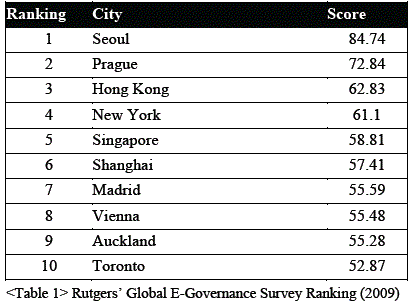
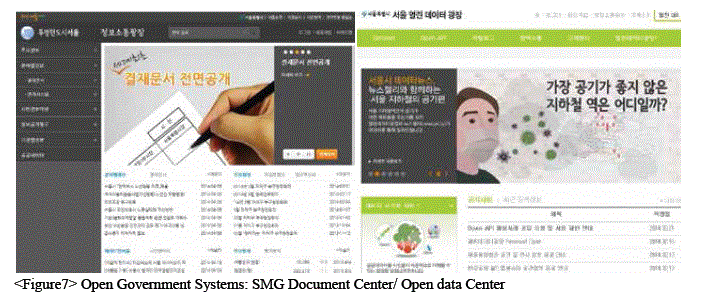
Disclosure of Public Information
“Open Government 2.0” has been created to push forward public participation in civil administrative services, disclosure of city documents and creation of an extensive public database.The system is expected to create greater understanding between the citizens and SMG staff and promote growth of industries which benefit from public data, establishing Seoul as one of the most advanced smart cities in the world.